The Internet of Things has long since ceased to be a buzzword and has become ubiquitous. As things communicate with each other, numerous opportunities arise to significantly simplify life and work. What IoT is and how FROX and Noser Engineering can support companies on their entire IoT journey? We’ll explain it in this blog post with the aid of real projects, we executed for our customers.
What is IoT?
The term Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical objects that interconnect and exchange data via the Internet using technologies such as sensors and software. This way, physical and virtual objects work together. To do so, a large amount of data is collected and then analyzed and used. Thanks to this data, important insights about users can be gained, offering immense potential for exciting new business models and personalized products. The Internet of Things is one of the most important drivers of digital transformation.
IoT in the enterprise: goals and benefits of the Internet of Things
By enabling human-to-human and human-to-object, as well as object-to-object communication, the Internet of Things has many use cases in both the private and commercial sectors, but especially in the industrial sector. The key goals and benefits of IoT include:
- Efficient operations through automation of processes, e.g. faster, safer warehouse logistics with the help of transport robots or faster, more targeted processing of customer inquiries.
- Reduced operating costs thanks to optimized process flows, e.g. cost-efficient control of heating and ventilation systems in a building or monitoring of equipment remotely instead of on site (saving unnecessary travel costs)
- Increasing productivity through better utilization of production capacity, e.g. avoiding delays in production or increasing occupational safety (minimizing accidents at work and thus downtime)
- Increasing the quality of work by reducing susceptibility to errors, e.g. precise work of robots when assembling workpieces or automated inspection of feed containers to ensure that they are filled (avoiding manual errors)
- Quality assurance, e.g., by monitoring and maintaining production machinery or maintaining food temperatures throughout the supply chain
- Improving customer experience through personalization, e.g. online tracking of deliveries or controlling the coffee machine remotely (convenience in everyday life through convenient coffee procuction from a smartphone)
- Opening up new business models and strengthening competitiveness, e.g. by manufacturing special parts using 3D printing or autonomous driving
Is investing in IoT worth it?
Various recent studies show that the added value of IoT projects is materializing faster and faster. Companies are already seeing measurable success immediately or within a few months. With each IoT project, they gain more experience and ideas for further projects to improve business areas or even open up new business models. Studies also show that companies give priority to working with external specialists when implementing IoT projects. As experts, they provide support with their experience and comprehensive know-how in the areas of consulting, project management, selection and implementation of IoT platforms, and software development, thereby offering companies the resources they need to realize IoT projects.
IoT Journey: with FROX and Noser Engineering from IoT to new business models and services
The digitization experts FROX and Noser Engineering are just such specialists who support companies in the implementation of their IoT projects. With modern technologies and the necessary competencies, the two companies of the Noser Group realize ideas and visions and increase the competitiveness of companies. From consulting and development to implementation, operation and support, companies receive everything from a single source. FROX and Noser Engineering lead companies through all steps of the IoT journey.
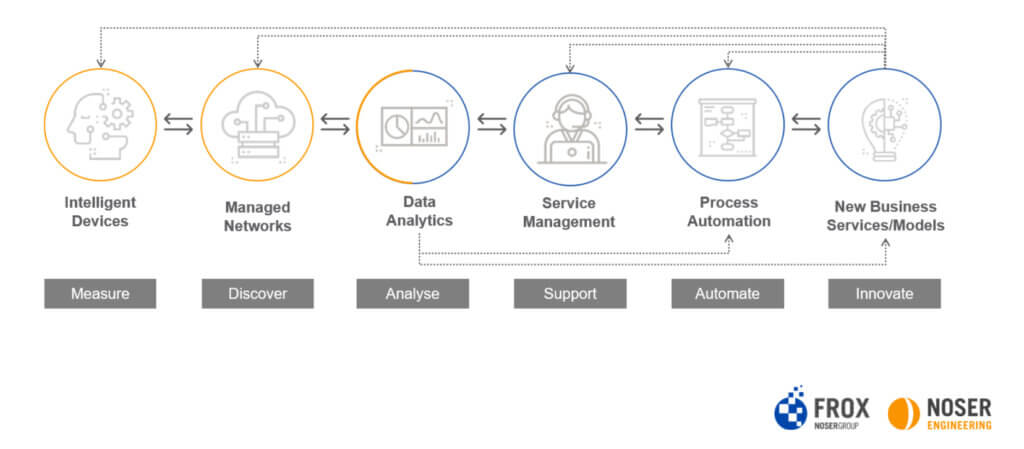
Internet of Things: Intelligent Devices
Services
- Evaluation of devices and components
- Development of embedded hardware/firmware according to IEC/ISO standards
- Integration of sensors
- Ensuring safety and security
- Consideration of real-time requirements
- Cost-effective proof-of-concepts
- Support up to series production
Benefits
- Connection of new/existing devices/machines to the internet
- Optimal solution for scaling applications
Method
- Implementation with the help of a specialized embedded team (more than 40 ETH and UAS engineers)
- Use of modern processor platforms such as ARM or STM
- Agile development approach
Use Case (example)
Sensirion: Nubo air monitoring system
Internet of Things: Managed Networks
Services
- Implementation of secure real-time communication with technologies such as BLE, LAN, WLAN, Zigbee, LORA, NFC, RFID and Powerline Communication (PLC)
Benefits
- Data communication from embedded devices to the cloud or to on-site storage devices
- Download of configuration data and firmware updates
- Highest data security
Method
- Implementation with the aid of technologies such as IP, SSL, MQTT and COAP
- Implementation of security audits, external audits and certifications (METAS)
Use Case (example)
Internet of Things: Service Management
Services
- Incident und Change Management
- Event Management (Predictive Maintenance)
- Asset und Configuration Management
- Field Service Management
- Service Level Management
Benefits
- End-to-end-service-view
- Higher service quality
- Increased productivity
- Improved customer experience
- Reduction of costs
Method
- Implementation using best-in-class service management solutions from leading vendors such as BMC Software and ServiceNow
Use Case (example)
Mobiliar Insurances: service desk seamlessly integrated without media disruption
Internet of Things: Data Analytics
Services
- Professional consulting for data analysis
- Extraction of information
- Analysis of problems, errors and anomalies
- Interpretation of data sets
- Generation of optimization potentials
- Development of a Big Data solution concept based on specific needs
Benefits
- Efficient use of large amounts of data from different sources and systems
- Better understanding of data
- Model building
Method
- Implementation using established technologies such as Azure, AWS, Google Cloud and Power BI
Use Case (example)
Midor: sugar, flour and industry 4.0
Internet of Things: Business Process Automation
Services
- Digitalization of customer-specific processes
- End-to-end process automation
- Integration in existing system landscape
- Innovative solution for a digital customer service
Benefits
- High process efficiency
- Fast process handling
- High quality of data and services
- Reduction of costs
- Positive customer experience
Method
Use Case (example)
BKW: Process solution in network services
Internet of Things: new business services/models
Services
- Strengthening the business model for digitization in the customer segment
- Gradual expansion and development of the range of offerings into digitized solution modules
- Alignment of service offerings with digitized end-to-end service delivery
Benefits
- Increasing sustainable competitiveness as well as service and process quality
- Development of new business areas, establishment of new billing models, use of digitalization potentials
- Improving time-to-market with new solution portfolios
- Flexibility and agility to anticipate changing market needs
Method
- Predictive Maintenance, Condition Monitoring, AI/KI, Machine Learning, XaaS, Pay-per-Use, Device Management, Download Configuration/Firmware
- Elimination of media disruption
- Methodical review of the enterprise model for credible digitization performance
- Focusing of digitization approaches in the product and service area of customer potentials
- Selective implementation projects for better business results
Use Case (example)











